Organization
Overview
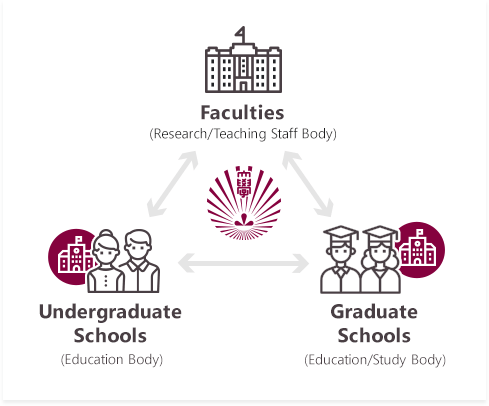
As part of this reorganization, the University has introduced a new Graduate School/Graduate Faculty system - the first attempt of this kind at a university in Japan.
By separating the former Graduate School into a Graduate School (education body) and Graduate Faculty (research body to which faculty members belong), the University is seeking to revitalize relationships between the Graduate Faculty and Graduate School, and Graduate Faculty and Undergraduate School.
It is also hoped that these changes will promote more dynamic functioning of the Graduate Faculty in relation to the Graduate and Undergraduate Schools.
All members of teaching staff of the agricultural research and education department now belong to the Faculty of Agriculture, all undergraduate students belong to the School of Agriculture, and all Master’s and Doctor’s course students belong to the Graduate School of Bioresource and Bioenvironmental Sciences.
In addition, a numbers of institutes in Kyushu University, but independent from the Faculty of Agriculture, have also merged with the Graduate School of Bioresource and Bioenvironmental Sciences; namely, the Biotron Institute, the Institute of Tropical Agriculture (in part), and the Bio-Architecture Center.
Organization chart
Faculty of Agriculture
| Department of Bioresource Sciences | Course | Agrobiological Sciences |
|---|---|---|
| Animal and Marine Biosciences | ||
| Department of Agro-environmental Sciences | Course | Bioproduction Environmental Sciences |
| Forest Environmental Sciences | ||
| Sustainable Bioresources Science | ||
| Department of Agricultural and Resource Economics | Course | Agriclutual and Resource Economics |
| Department of Bioscience and Biotechnology | Course | Molecuar Biosciences |
| Systems Bioengineering | ||
| Food Science and Biotechnology | ||
| [Endowed Chairs and funded Research Departments] Laboratory of functional water, food and energy | ||
| [Endowed Chairs and funded Research Departments] Bioactive Polysaccharide Analysis | ||
| Institute of Biological Control | ||
| Institute of Genetic Resources | ||
| Center for Promotion of International Education and Research, Faculty of Agrlculture | ||
| Innovative Bio-Architecture Center | ||
| Insect Science and Creative Entomology Center | ||
Attached organization
University Farm
The main fields of the University Farm are located in Kasuya-machi about 6 km from the Hakozaki campus area, and comprise 24 ha of arable lands. In addition to these main fields, 8.3 ha of an orchard and 11 ha of pastures are maintained in the Kasuya Research Forest, University Forests.
The Kuju Agricultural Research Center, which is located in the center of the Kuju Highlands, is also the facility of the University Farm. It comprises 78 ha of pasturelands at an altitude of about 900 m.
The University Farm has excellent facilities for both field instruction and researches on paddy field agriculture, horticulture and animal husbandry.
Diverse experiments on cultivating agricultural crops and raising domestic animals are conducted, as well as those on developing systems for sustainable agriculture.
University Forest
The University Forest is composed of the following three forests:
The Kasuya Research Forest (481 ha) is located in towns of Sasaguri and Hisayama, Fukuoka Prefecture, about 32 km east of the Ito campus of Kyushu University. Over 60% of the forest area is covered by plantation forests, and the rest of forest area are natural forests consist of warm-temperate evergreen trees. The Sawara Training Forest (32 ha) located along the western Hakata Bay in Fukuoka City, in which Pinus sp. is dominant species, is comprised in the Kasuya Research Forest.
The Shiiba Research Forest (2,917 ha) is located in Shiiba Village, Miyazaki Prefecture, the central area of Kyushu mountain ranges. The forest area is mainly covered by natural forests consist of the mixed forest of deciduous broadleaf trees and conifers. Only 18% of forest area is occupied by plantation forest.
The Ashoro Research Forest (3,711 ha) is located in Ashoro Town, eastern Hokkaido. About 60% of forest area is covered by natural forests consist of cool-temperate deciduous broadleaf trees. The rest of forest area is occupied by plantation forests.
These forests covered major vegetation zones in the Japanese archipelago are utilized not only for the educations and researches on forest sciences but also biology, environmental sciences and so on. They are also utilized for hands-on learning program for citizen and children.
Fishery Research Laboratory
The Fishery Research Laboratory was established in 1944, as one of the attached institutions of Kyushu University. This laboratory is located on the Tsuyazaki coast (about 25 km north of Fukuoka City), facing the sea of Genkai. Staff in the laboratory are mainly concerned with subjects relating to fisheries science: fish ecology, fish physiology, aquaculture and fry production of marine animals. Research facilities including two research vessels and accommodation are also offered to researchers and students who may wish to visit and carry out research and/or experiments. The laboratory has its own academic journal titled Report of Fishery Research Laboratory, Kyushu University, as an irregular publication.
Institute of Biological Control
Institute of Biological Control concentrates on microbial control of insect pests, bacterial opportunistic pathogens of insects, protozoa infection in insects, defense reaction of insects to microbial diseases, biological control of arthropod pests with parasitoids and predators, ecology of parasitoids and predators, biological control of citrus scale pests and biological control of greenhouse pest.
Institute of Genetic Resources
The institute is devoted to basic and applied studies on genetics with special interest in the stock maintenance of agriculturally important organisms, silkworm, rice and fermentative microbes. Emphasis has also been placed on the studies at molecular levels to contribute to the development of biotechnology and to establish the gene libraries of these biological resources.
Center for Promotion of International Education and Research, Faculty of Agriculture
In emerging Southeast Asian countries, water and soil quality deterioration and other environmental problems related to agriculture-forestry-fishery production infrastructure have grown more serious due to rapid population growth and economic development. Sea level elevation and precipitation changes accompanying climate change and global warming have also become serious problems that threaten stable production. While the expansion of food production is urgently required for poverty reduction and food security in the world, the situation is growing even more serious. At the same time, biodiversity loss has become a serious issue. Genetic diversity loss for crops and farm animals has also become a major issue through the expanded adoption of high-yield varieties for boosting food output. The world is thus urgently required to balance biological production expansion and environment and biodiversity conservation. However, science and technology levels in many developing countries are not high enough to solve these challenges. The assistance of Japan and other developed countries is urgently required. While Japan has seen production infrastructure deterioration in rural regions in the postwar period, Southeast Asian emerging countries have recently begun to rapidly experience a similar phenomenon accompanied by water and soil environment deterioration due to climate change and global warming. Given that an urgent challenge is to conserve the water and soil environment as life infrastructure while maintaining high productivity, the Faculty of Agriculture will enhance global research in full cooperation with overseas universities, building on its accumulated research achievements. The Promotive Center for International Education and Research of Agriculture play a central role in this initiative.
Innovative Bio-Architecture Center
Innovative Bio-Architecture Center ( i -BAC), has been established in April 2015 by reorganizing the Bio-Architecture Center (KBAC), which was founded in 2005 and had functioned as a center for strategic research promoting postgenome omics sciences in Kyushu University. Based on achievements in basic and applied biological researches at KBAC, i-BAC aims to advance two novel research areas, industrial biomaterial/bioenergy design and positive health design. The center comprises two divisions, “Biomaterials” and “Metabolic systems”, and has been committed to promote education of these research areas in the Undergraduate and Graduate school of Bioresource and Bioenvironmental sciences in the University
Insect Science and Creative Entomology Center
Insect Science and Creative Entomology Center was established in April 2018, to overcome issues such as loss of biodiversity and the spread of insect-borne infectious diseases that modern society faces, by integrating the insect sciences of Kyushu University and creating a new “knowledge”.
In particular, there are three major problems concerning insects in
modern society
• Lack of scientific basis that can respond to loss of global biodiversity
•Exhaustion of human resources and education systems working on insect-borne infectious diseases including emerging infectious diseases
•Inefficient industrialization of unique insect technology seeds from university
This center consists of 3 units, insect taxonomy, environment and hygiene entomology, and creation of new insect industry. The aim of this center is to establish a global research and education center that can contribute to the well-being of humanity.
Center for Advanced Instrumental and Educational Supports, Faculty of Agriculture, Kyushu University
Center for Advanced Instrumental and Educational Supports, Faculty of Agriculture, Kyushu University
Hikosan Biological Institute
Hikosan Biological Institute
Fisheries Research Institute of Karatsu Department of Joint Research
The goal of this department is to promote utilization of new marine resources and advancement of fisheries and aquaculture technologies. Our research programs cover physiology, nutrition, embryology, ecology, biotechnology and molecular biology concerning development of aquaculture technologies including breeding and seed production. This department also aims to distribute the developed technologies in order to revitalize regional fisheries industry through industry-university-government collaborations.

